Our Treatment
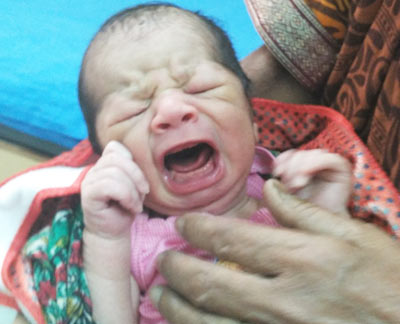
Excessive Crying
Excessive crying in children, especially infants, can be challenging for parents to handle. Common causes include hunger, fatigue, discomfort, or a need for attention. It could also indicate underlying issues like colic, teething, or illness.
What to Do
- Ensure your child is fed, clean, and comfortable.
- Look for symptoms of illness like fever, rash, or unusual behavior, and consult a pediatrician if needed.
If crying persists despite addressing these needs or is accompanied by unusual symptoms, seek medical advice promptly.
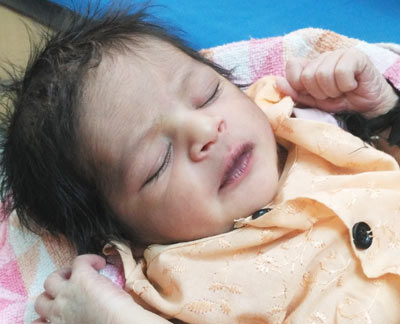
Jaundice
Jaundice is a common condition in newborns, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels. It typically appears within the first week after birth and often resolves without treatment.
What to Do
- Keep track of the yellowing and baby's feeding patterns.
- Encourage regular breastfeeding or formula feeding to help flush bilirubin.
Consult a pediatrician if jaundice worsens, lasts beyond two weeks, or is accompanied by poor feeding, lethargy, or dark urine. Phototherapy or other treatments may be needed in severe cases.

Fever
Fever is a common response to infection and indicates the body is fighting illness. It is defined as a body temperature above 100.4°F (38°C).
What to Do:
- Use a thermometer to confirm fever.
- Encourage fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Dress lightly, use a lukewarm sponge bath, or provide fever-reducing medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen (as per doctor’s advice).
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain in children is a common complaint and can have various causes, ranging from mild to serious.
What to Do:
- Note the location, duration, and severity of the pain.
- Check for vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or changes in behavior.
Seek immediate medical attention if the pain is severe, localized (e.g., lower right abdomen), or accompanied by fever, persistent vomiting, or blood in stool.
Loose Motions
Loose motions (diarrhea) in children are common and usually caused by infections or dietary changes.
What to Do:
- Give oral rehydration solutions (ORS) to prevent dehydration.
- Offer bland foods like rice, bananas, and applesauce. Avoid sugary or greasy foods.
- Watch for signs of dehydration like dry mouth, reduced urination, or lethargy.
Consult a doctor if diarrhea lasts more than 2 days, includes blood or mucus, or is accompanied by fever, severe abdominal pain, or signs of dehydration.
Feeding Problems
Feeding problems in children can arise at any age and may include refusal to eat, limited diet, or difficulty swallowing.
- Set regular meal and snack times.
- Introduce a range of healthy foods without forcing.
- Ensure a calm eating environment.
- Look for signs of pain, discomfort, or difficulty swallowing.
Consult a pediatrician if feeding issues persist, the child shows poor growth, frequent vomiting, or symptoms like choking or gagging during meals.
Breathing Difficulty
Breathing difficulty in children can be alarming and requires prompt attention.
What to Do:
- Keep the child relaxed.
- Check for obstructions and encourage coughing.
- Use a cool mist humidifier or sit in a steamy bathroom.
Seek emergency medical care if the child struggles to breathe, cannot speak or cry, has bluish skin, or shows signs of severe distress.
Constipation
Constipation in children is common and often results from dietary habits, dehydration, or lack of physical activity.
What to Do:
- Add fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to meals.
- Ensure the child drinks plenty of water.
- Promote regular physical play or exercise.
Consult a doctor if constipation lasts more than two weeks, is accompanied by severe pain, blood in stools, or if the child stops eating or growing normally.


